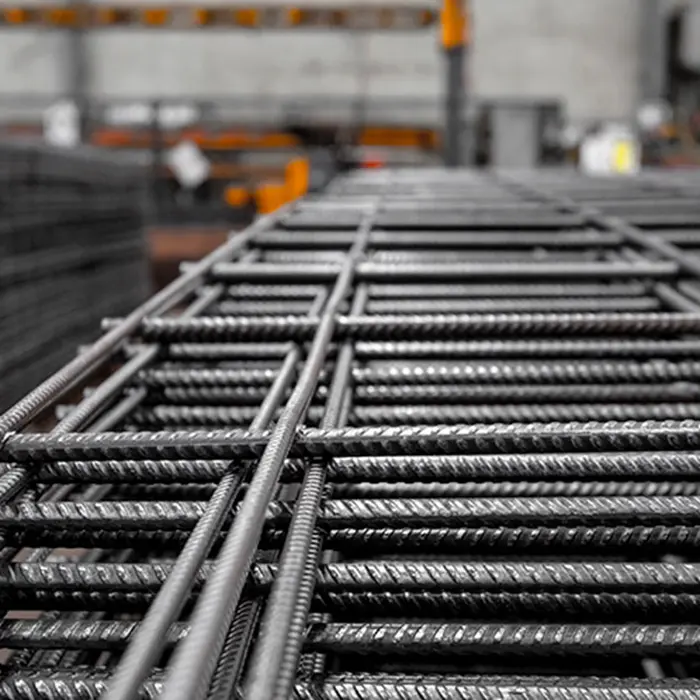
Reinforcing mesh, also known as rebar mesh or welded wire mesh, is a prefabricated grid of steel wires used to strengthen concrete structures. Composed of longitudinal and transverse bars welded together at regular intervals, it provides uniform tensile strength to counteract concrete's natural weakness against cracking and bending forces. This construction material is widely used in slabs, walls, pavements, and foundations to enhance structural integrity and durability.
The mesh comes in various wire thicknesses and grid patterns, allowing engineers to select specifications based on load requirements. Unlike loose rebar that requires manual tying, reinforcing mesh offers faster installation with consistent spacing, reducing labor costs and construction time. Its welded joints maintain precise alignment during concrete pouring, ensuring even stress distribution. Galvanized or epoxy-coated variants are available for projects requiring corrosion resistance in harsh environments.
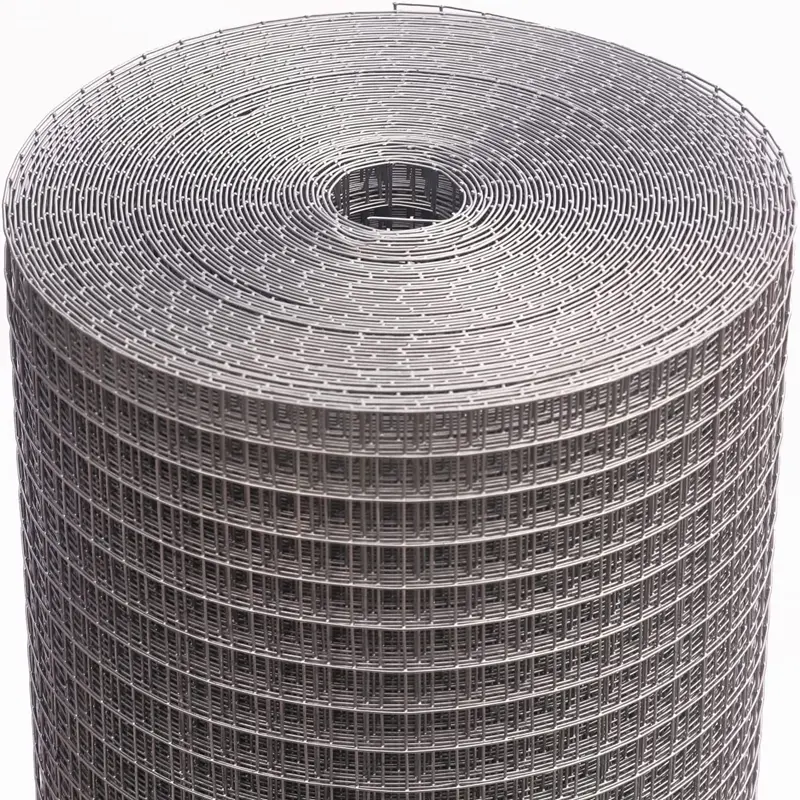
Galvanized vs Epoxy Coated Reinforcing Mesh
Galvanized reinforcing mesh undergoes a hot-dip zinc coating process, creating a protective barrier against corrosion while maintaining the steel's structural integrity. This makes it ideal for outdoor or high-moisture environments like coastal areas or bridges, where rust resistance is critical. The zinc layer also provides sacrificial protection, meaning it corrodes before the underlying steel, extending the mesh's lifespan.
Epoxy-coated reinforcing mesh features a fusion-bonded polymer layer applied electrostatically, offering superior chemical resistance, particularly against chlorides in concrete or road salts. While more expensive than galvanized mesh, it excels in harsh industrial settings or road constructions where de-icing salts accelerate corrosion. However, the epoxy coating can be vulnerable to installation damage, requiring careful handling. The choice depends on budget, environmental exposure, and project specifications, with galvanized mesh being more cost-effective for general use and epoxy-coated preferred for extreme conditions.
Applications of Reinforcing Mesh in Building, Road, and Bridge Construction
Reinforcing mesh is indispensable in modern construction for enhancing tensile strength and preventing cracks. In building construction, it stabilizes concrete slabs, walls, and foundations, ensuring load distribution and minimizing shrinkage cracks during curing. For road construction, welded wire mesh or epoxy-coated grids reinforce pavements and airport runways, reducing rutting and extending service life under heavy traffic.
In bridge construction, galvanized or epoxy-coated mesh is used in decks, abutments, and barriers to withstand dynamic loads and environmental stress. Its grid structure also simplifies installation compared to rebar, speeding up projects. From precast concrete elements to seismic-resistant structures, reinforcing mesh ensures durability and safety across infrastructure projects, adapting to varying demands through material and design innovations.