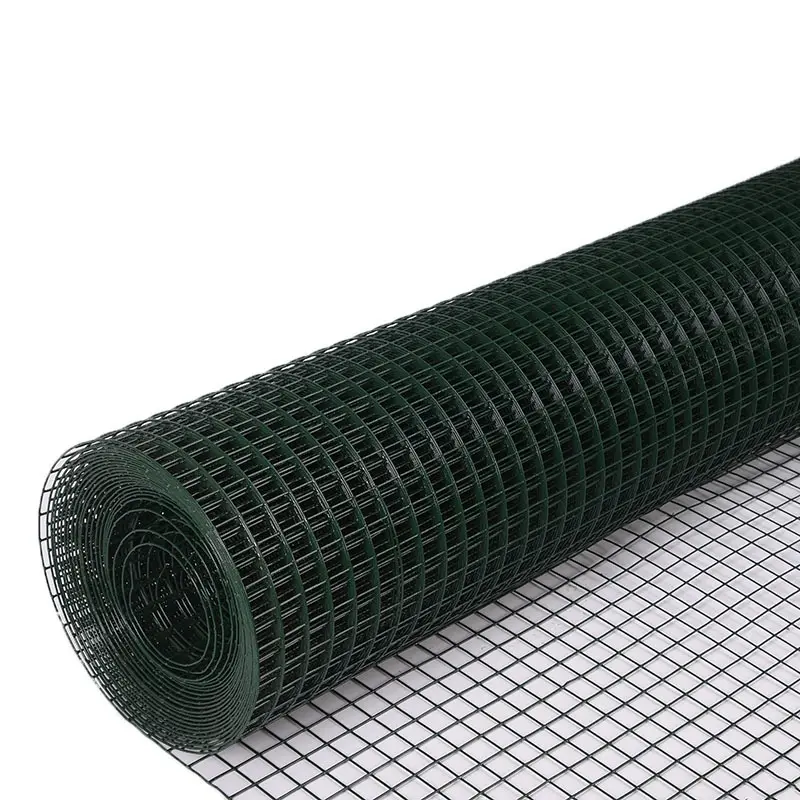
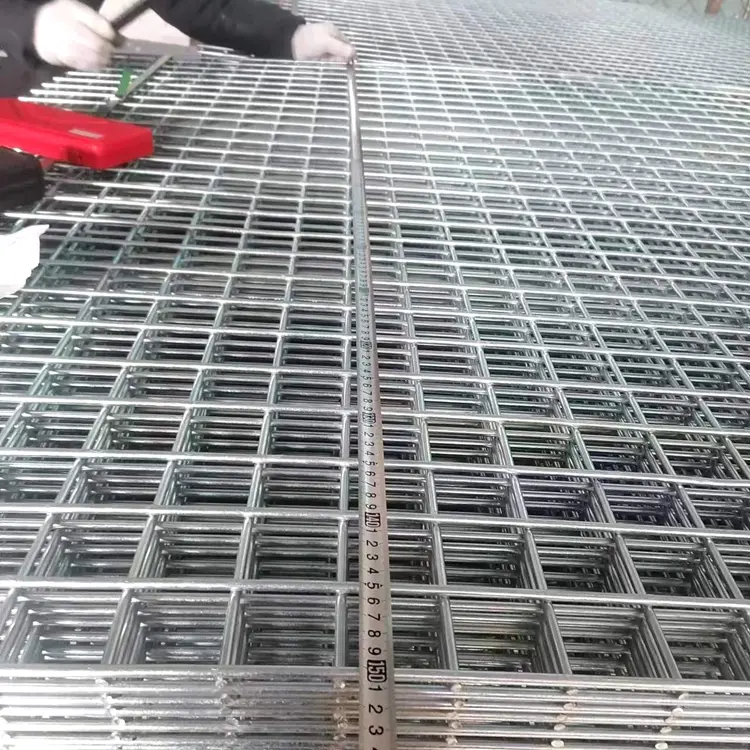
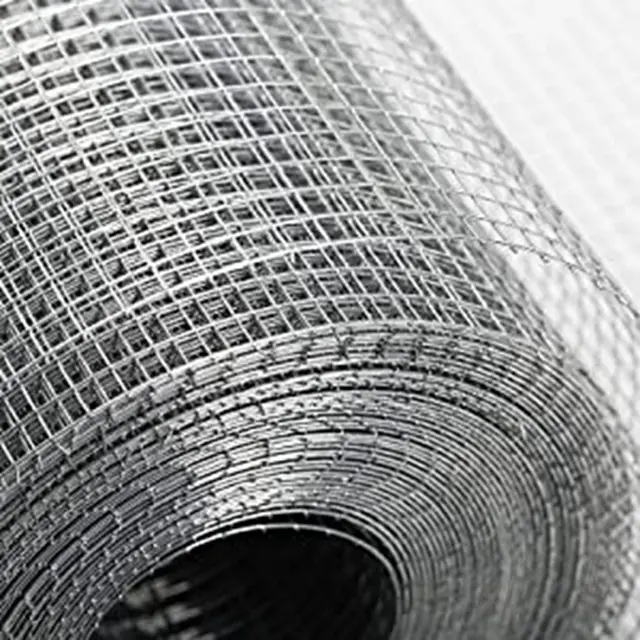
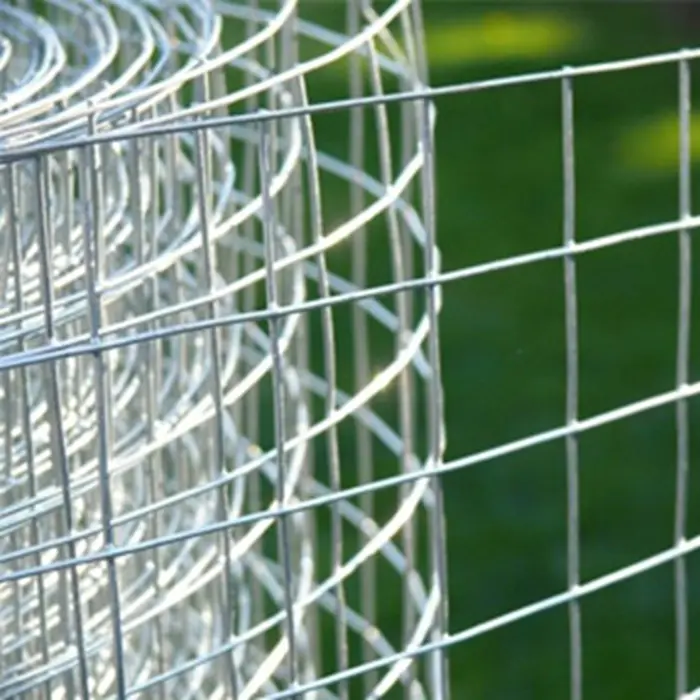
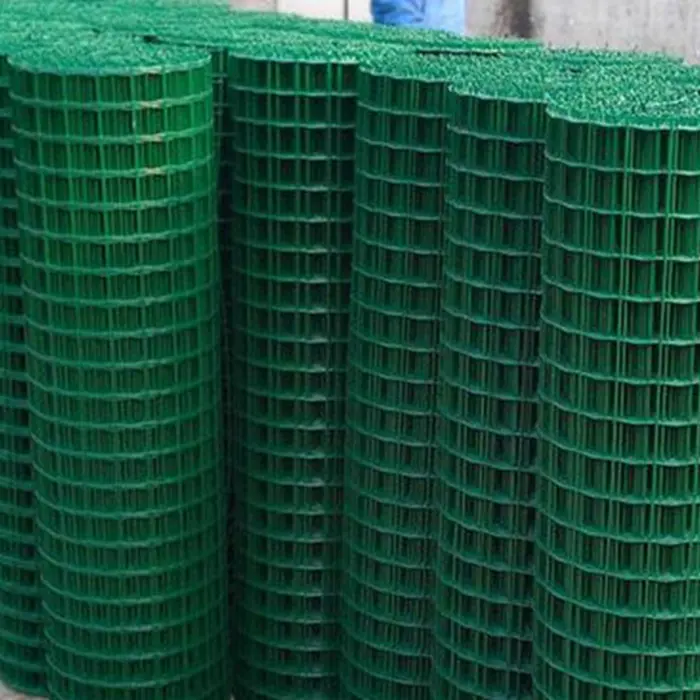
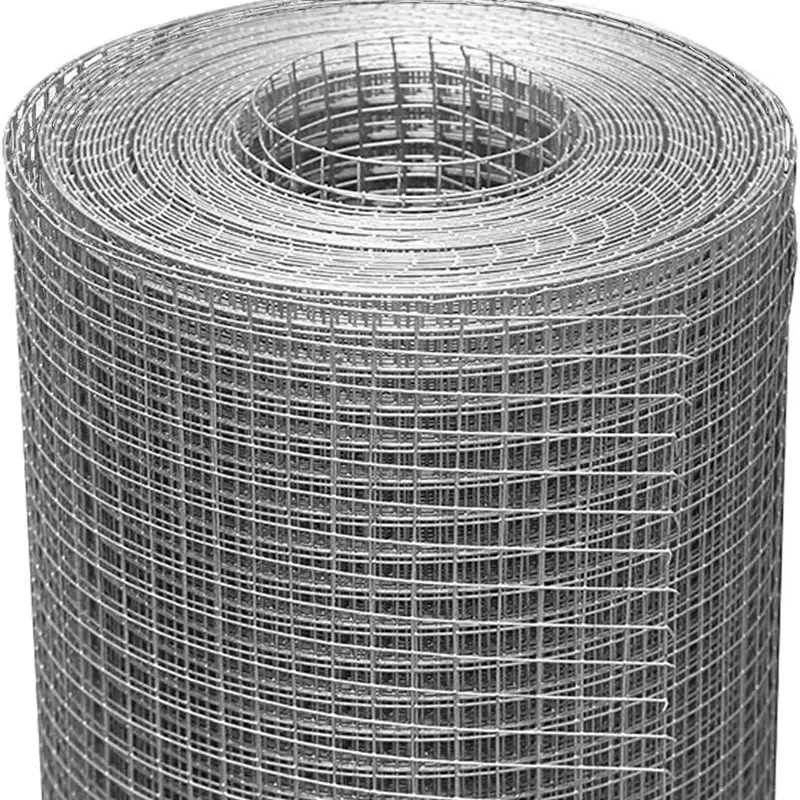
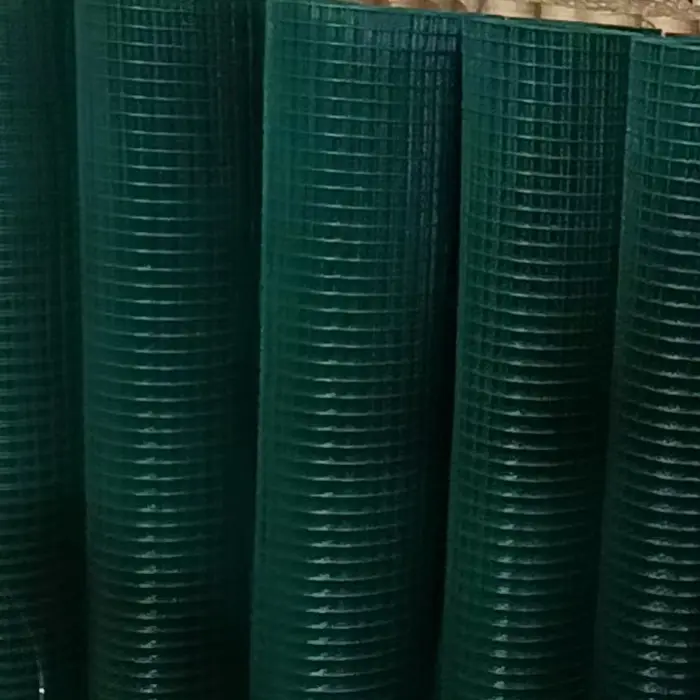
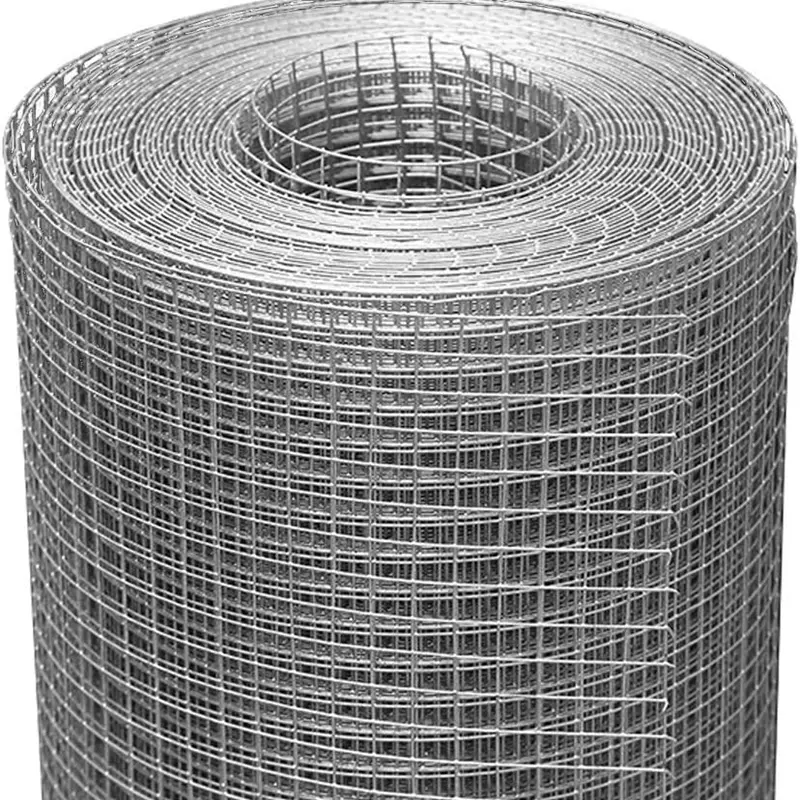
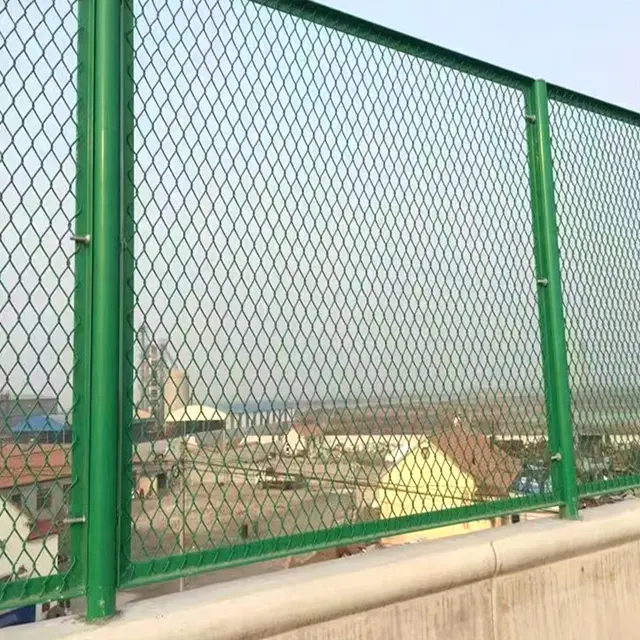
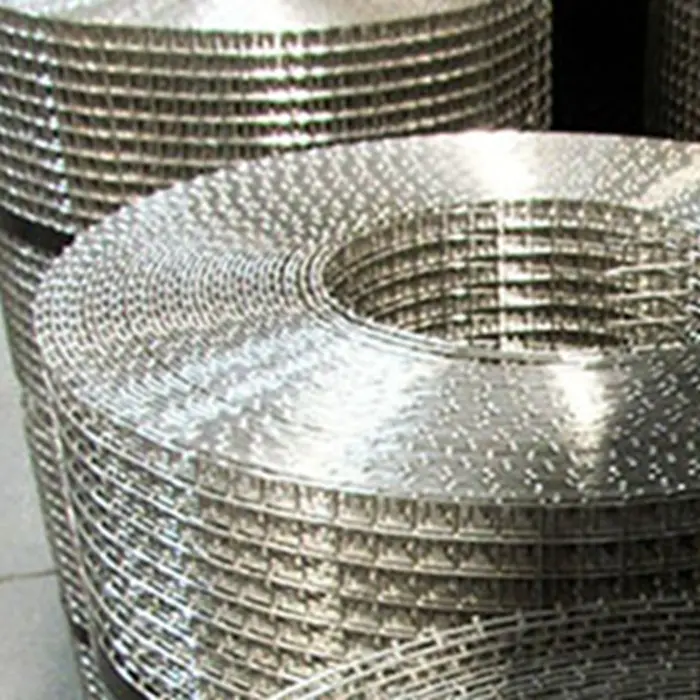
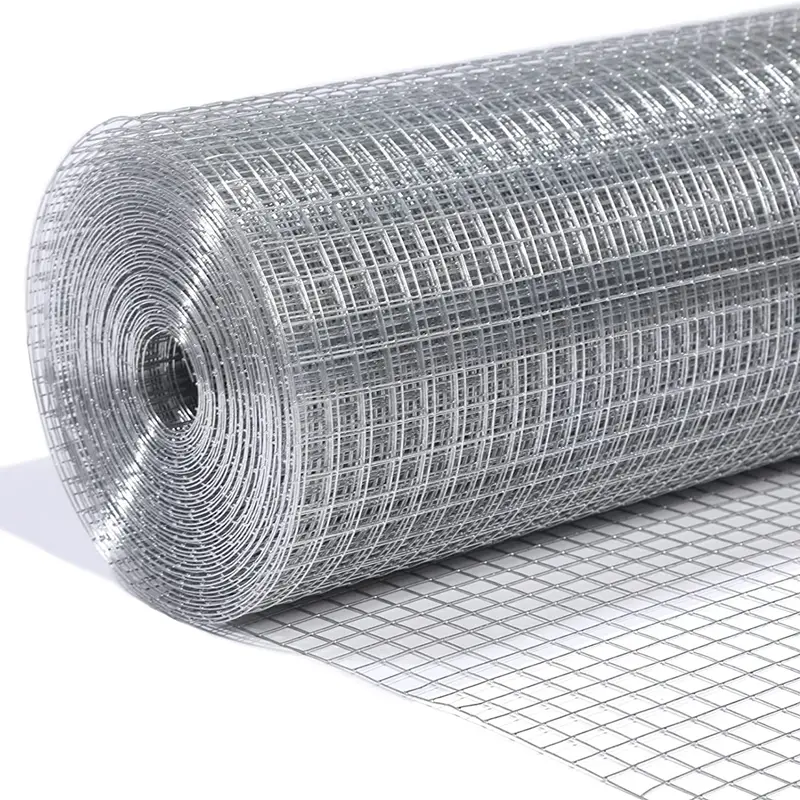
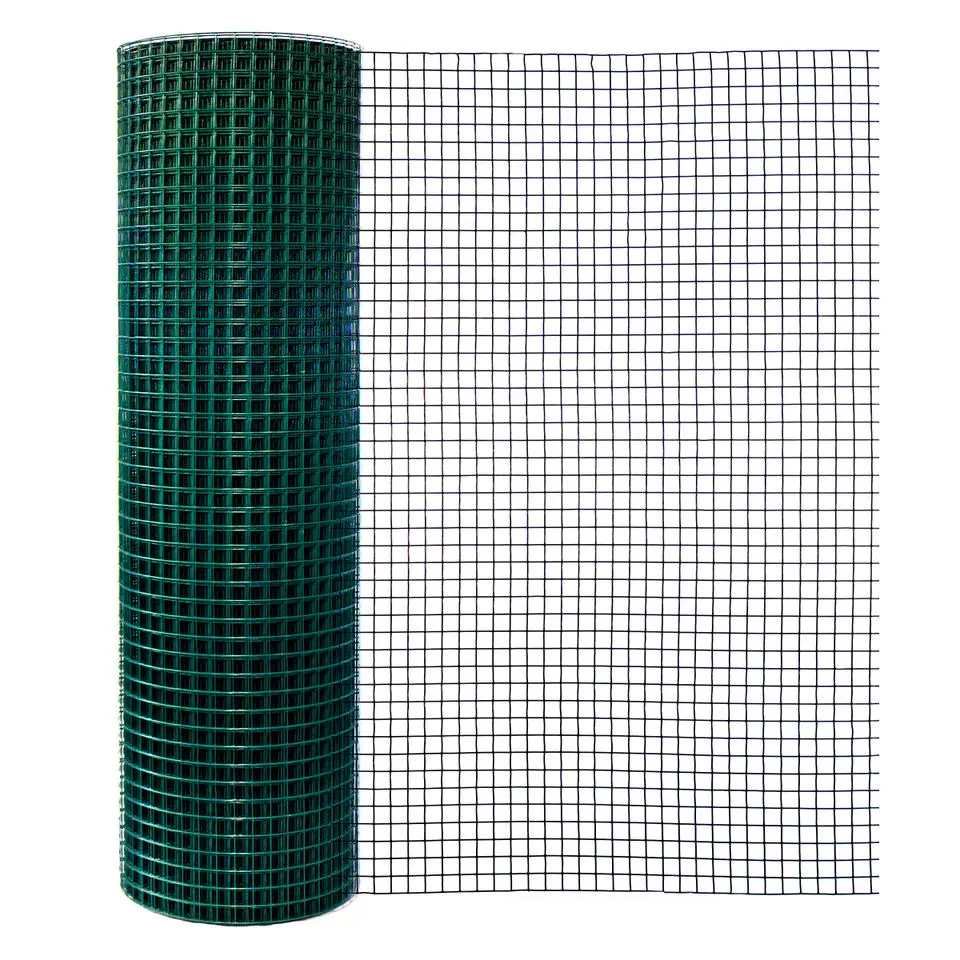
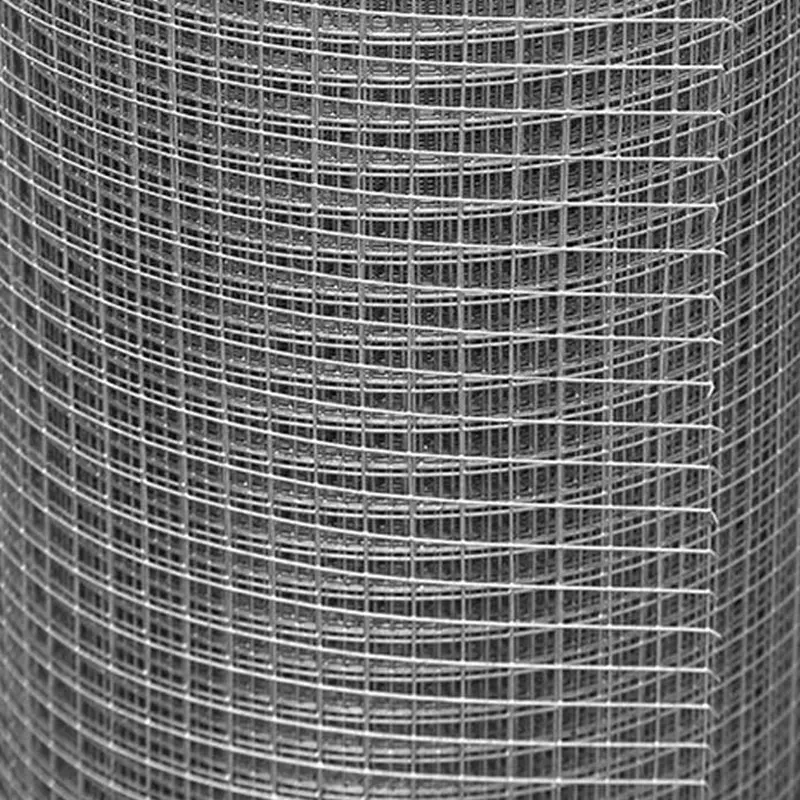
Welded Wire Mesh is a durable and versatile construction material formed by welding intersecting steel or stainless steel wires at right angles to create a uniform grid pattern. Known for its strength and rigidity, our welded mesh for sale is widely used in industrial, agricultural, and architectural applications. The welding process ensures a sturdy, fixed structure that resists bending or separation, making steel welded wire ideal for concrete reinforcement, fencing, and machine guards.
Beyond functionality, welded wire mesh is valued for its clean, geometric appearance, often used in modern architectural designs for facades, partitions, or decorative screens. Easy to install and low-maintenance, our iron welded mesh offers a cost-effective solution for projects demanding both strength and precision. Its adaptability and reliability make it a staple in infrastructure, security, and design applications worldwide.
What is the Difference Between Welded Mesh and Expanded Mesh?
Welded mesh and expanded mesh are distinct in production method, structure, and application. Welded mesh is made by electrically welding intersecting steel wires at precise right angles, creating uniform square or rectangular openings. This results in a rigid, stable grid ideal for applications requiring high strength and security, such as fencing, concrete reinforcement, and industrial partitions.
Expanded mesh,also known as expanded diamond mesh, by contrast, is produced by cutting and stretching a single metal sheet, forming a diamond-shaped pattern with interconnected strands. This creates a flexible yet durable material with no welded joints, making it resistant to unraveling. Expanded mesh is lighter and more adaptable for architectural facades, walkways, and decorative screens, where airflow and aesthetics are priorities. While welded mesh excels in load-bearing precision, expanded mesh offers versatility and material efficiency.
Welded Wire Mesh Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of welded wire mesh involves four key stages: wire drawing, mesh welding, treatment, and finishing. First, steel rods are cold-drawn to achieve precise diameters. These wires are then fed into an automated welding machine, where electrical resistance welding fuses them at cross points under high heat and pressure, ensuring consistent spacing and strength.
After welding, the mesh undergoes surface treatment—typically galvanizing or PVC coating—to enhance corrosion resistance. Finally, panels are cut to size, rolled, or stacked for shipment. Advanced CNC-controlled systems allow customization of wire thickness, mesh size, and panel dimensions to meet specific project needs. This efficient process yields a high-strength, uniform product widely used in construction, agriculture, and security fencing.